Biography
I graduated from School of Pharmacy, Mansoura University, Egypt in 1999 then completed my MSc in Immunology in 2004 at the same school. In 2009 I was awarded my PhD in Immunology and inflammation from School of Medicine, University of Leicester, UK. From 2010 until 2014 I had a postdoctoral research position in the same department. From 2015 until 2018, I was working as an associate professor of Immunology at the department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mansoura University, Egypt. Now I am a senior research associate at the department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Cambridge since 2019.
Research
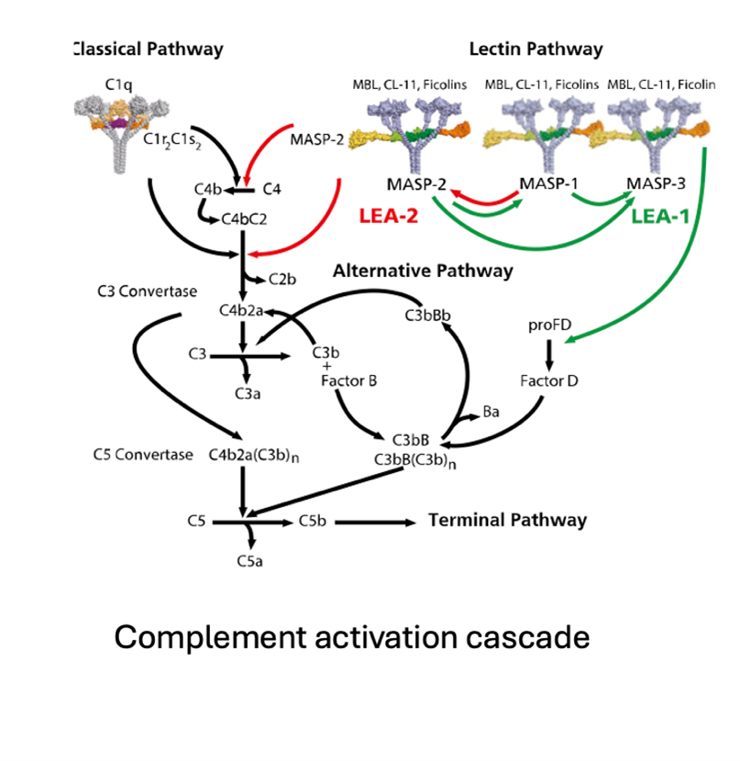
Complement system, an important component of innate immunity. Three independently operating activation pathways, called the Classical, the Lectin or the Alternative Pathways drive this system. Each activation pathway can contribute to very specific pro-inflammatory conditions that manifest in various diseases and my present research aims to further define the predominant pathway specific contributions towards complement mediated inflammatory pathology. My research focused on the development of new complement therapeutic inhibitors that can be used in the treatment of inflammatory disorders. These inhibitors were shown to be highly effective in ameliorating the severity of thrombotic disease conditions, such as Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMAs), renal TMAs (such as IgA nephropathies), Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI). Our new findings showed that these inhibitors are highly effective in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) associated with SARS-COV-2 and H1N1 infections. In addition, we are now developing a new therapeutic approach and reagents that will enhance complement mediated microbial killing. These reagents are highly potent recombinant bi-specific antibodies that eradicate bacteria via complement mediated lysis and phagocytosis.
Publications
https://scholar.google.co.uk/citations?user=T7sm2aoAAAAJ&hl=en
Recent publications
- Ali YM, Carnell GW, Fumagalli S, Mercurio D, Seminara S, Lynch NJ, et al. Inhibition of the Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation Reduces Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Severity in a Mouse Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J Infect Dis (2024) 229:680-690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad462.
- (3) Ali YM, Lynch NJ, Shaaban AA, Rizk DE, Abdel-Rahman SH, Khatri P, et al. Inhibition of the lectin pathway of complement activation reduces LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. Front Immunol (2023) 14:1192767. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1192767.
- Ali YM, Lynch NJ, Khatri P, Bamigbola IE, Chan ACY, Yabuki M, et al. Secondary Complement Deficiency Impairs Anti-Microbial Immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus During Severe Acute COVID-19. Front Immunol (2022) 13:841759.doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.841759.
- Ali YM, Ferrari M, Lynch NJ, Yaseen S, Dudler T, Gragerov S, et al. Lectin Pathway Mediates Complement Activation by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Front Immunol (2021) 12:714511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.714511.
- Ali YM, Hayat A, Saeed BM, Haleem KS, Alshamrani S, Kenawy HI, et al. Low-dose recombinant properdin provides substantial protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2014) 111:5301-5306. doi:10.1073/pnas.1401011111.
- (8) Ali YM, Ferrari M, Lynch NJ, Yaseen S, Dudler T, Gragerov S, et al. Lectin Pathway Mediates Complement Activation by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Front Immunol (2021) 12:714511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.7145117.
- (9) Shehab El-Din EMR, Elgaml A, Ali YM, Hassan R. Inhibition of the Classical Pathway of Complement Activation Impairs Bacterial Clearance during Enterococcus faecalis Infection. Infect Immun (2021) 89:e00660- 20. Print 2021 Apr 16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00660-20.