Extracellular Vesicle Research Group
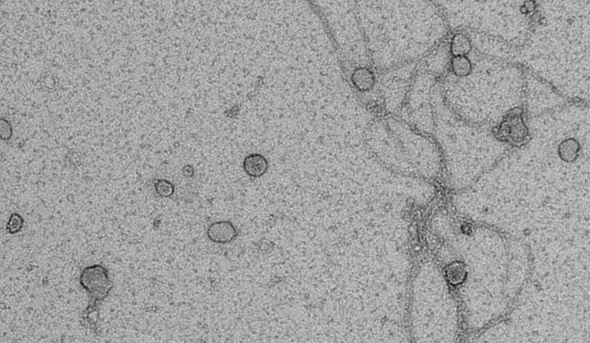
Extracellular vesicles (including exosomes) are nanovesicles released by cells, which contain proteins, mRNAs and microRNAs. In non-renal contexts they have various physiological functions including inter-cellular transfer of proteins and RNA, facilitation of immune responses, and modulation of the anti-apoptotic response. Urinary extracellular vesicles are also a rich source of potential biomarkers, since their membranes are composed of apical proteins from all nephron segments and they contain nucleic acid and protein cargo from the cell of origin.
I am currently a visiting research fellow in the Karet laboratory (Cambridge Institute of Medical Research), and our laboratory has demonstrated that urinary exosomes are bactericidal (Hiemstra et al, 2014), and contain microRNAs (miRNAs) capable of paracrine modulation of tubular membrane transporters in vitro (Gracia et al, 2017). The current focus of my research is to investigate two properties of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are relevant to renal and urinary tract disorders, namely; the utility of EVs as a source of biomarkers of renal diseases, and the clinical significance of the bactericidal activity of urinary exosomes/EVs, although I also collaborate with other groups to investigate the biomarker potential and pathophysiological roles of EVs in other contexts (cancer, transplant rejection, cardiac disease and pain).
I am also interested in novel biomarkers for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in cats and urothelial cell carcinoma in dogs that might allow veterinarians to detect these diseases at an earlier stage. Our laboratory has recently identified differentially expressed proteins associated with EVs in cats with CKD and hypertension (Lawson et al, 2023) and identified urinary EV-associated miRNAs that are potential biomarkers for urothelial carcinoma in dogs (Karttunen et al, 2024).
Current group members:
Dr Tugdem Muslu-Ufuk (Postdoctoral research associate)
Lanhui (Monica) Qui (PhD student)
Collaborators:
Professor Fiona Karet (Department of Medical Genetics)
Dr Ashraf Zarkan (Department of Genetics)
Professor Ewan St-John Smith (Department of Pharmacology)
Professor Jose Novo Matos (Department of Veterinary Medicine)
Dr James Whitworth (Department of Medical Genetics)
Dr Massimiliano di Pietro (Department of Oncology)
Dr Vasilis Kosmoliaptis (Department of Surgery)
Dr Shubha Anand (Cambridge Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory)
Dr Jack Lawson (Royal Veterinary College)
Dr Claire Dixon (Tufts University)
Dr Russell Morphew (Aberystwyth University)
Dr Xiaonan Wang (Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China)